GPON (Gigabit Passive Optical Network) is an efficient fiber access technology primarily composed of two core devices: OLT (Optical Line Terminal) and ONT (Optical Network Terminal). Their functions in the optical line terminal network are as follows:
OLT (Optical Line Terminal)
The OLT is a device deployed at the service provider's central office. Its main functions include:
1. Optical-Electrical Conversion: The OLT converts electrical signals from the backbone or metropolitan area network into optical signals and sends them to the ONTs through the PON network.
2. Bandwidth Management: The OLT allocates bandwidth to each user, supporting Dynamic Bandwidth Allocation (DBA) to improve bandwidth utilization.
3. Traffic Aggregation and Forwarding: It aggregates upstream traffic from each ONT and forwards it to the upper layer network while distributing downstream traffic from the upper layer network to each ONT.
4. QoS (Quality of Service): The OLT provides various QoS mechanisms to ensure that different types of data have different priorities and bandwidth guarantees.
5. Network Management: Through the Network Management System (NMS), the OLT configures, monitors, and maintains the entire PON network, including fault detection and performance monitoring.
6. Security Functions: The OLT provides data encryption and user authentication to ensure the security of network communications.
ONT (Optical Network Terminal)
ONT is a device deployed at the user's premises. Its main functions include:
1. Optical-Electrical Conversion: The ONT converts the optical signals sent by the OLT into electrical signals for user devices (such as computers, TVs, etc.), and converts the electrical signals sent by user devices back into optical signals to be sent to the OLT.
2. Service Access: It supports access to various user services, such as internet access, IPTV, VoIP, etc., through Ethernet interfaces or Wi-Fi.
3. Bandwidth Control: It controls the bandwidth usage at the user end based on the OLT's bandwidth allocation strategy.
4. Local Management: It provides local management interfaces, allowing users to perform basic configuration and maintenance through a web interface or command line interface.
5. QoS (Quality of Service): It supports basic QoS functions to ensure the quality of different services at the user end.
6. Security Functions: It supports user authentication and data encryption to ensure the security of user data.
Features and Advantages of GPON Networks
· High Bandwidth: GPON provides symmetrical or asymmetrical high-speed data transmission, typically with a downstream bandwidth of 2.5Gbps and an upstream bandwidth of 1.25Gbps.
· Long Distance Coverage: GPON supports a maximum coverage range of 20 kilometers, making it suitable for widespread coverage in urban, suburban, and remote areas.
· Efficient Utilization of Fiber Resources: GPON adopts a point-to-multipoint architecture, using splitters to distribute a single fiber to multiple users, significantly reducing the cost of fiber resources.
· Flexible Service Support: GPON can support a variety of services, including data, video, and voice, meeting the diverse needs of both residential and business users.
Comparison between OLT and ONT
OLT (Optical Line Terminal)
· Function: The OLT is the core device in a GPON (Gigabit Passive Optical Network) system, located in the service provider's central office (CO). It communicates with multiple ONTs (Optical Network Terminals), managing and controlling the entire PON network, and forwarding signals from ONTs to the service provider's backbone network.
· Location: Typically located in a data center or the service provider's facility.
· Main Tasks:
1. Bandwidth allocation
2. Providing data, voice, and video services
3. Managing and maintaining the PON network
4. Interfacing with the core network
ONT (Optical Network Terminal)
· Function: The ONT is the terminal device in a GPON system, located at the user end. It converts optical signals into electrical signals that user devices can use, such as Ethernet, Wi-Fi, or telephone signals.
· Location: Installed at the end user's home or office.
· Main Tasks:
1. Receiving and transmitting optical signals
2. Providing local network connections (e.g., Ethernet ports, Wi-Fi)
3. Supporting various user services (e.g., internet access, IPTV, VoIP)
GPON OLT and ONT Ports
GPON OLT Ports
· PON Ports: Connect to the optical splitter (Optical Distribution Network), supporting up to 64 or 128 ONTs.
· Uplink Ports: Connect to the service provider's core network, typically gigabit or 10-gigabit Ethernet ports.
· Ethernet Ports: Used for local network management and maintenance.
· Control Ports: For network administrators to manage and configure the device.
GPON ONT Ports
· PON Port: Connects to the optical distribution network.
· Ethernet Ports (LAN Ports): Connect to the user's computer, router, or switch.
· Telephone Ports (POTS Ports): Connect to analog telephone devices.
· Wi-Fi: Provides wireless network connectivity (available on some ONT devices).
· Video Ports: Connect to a television or set-top box.
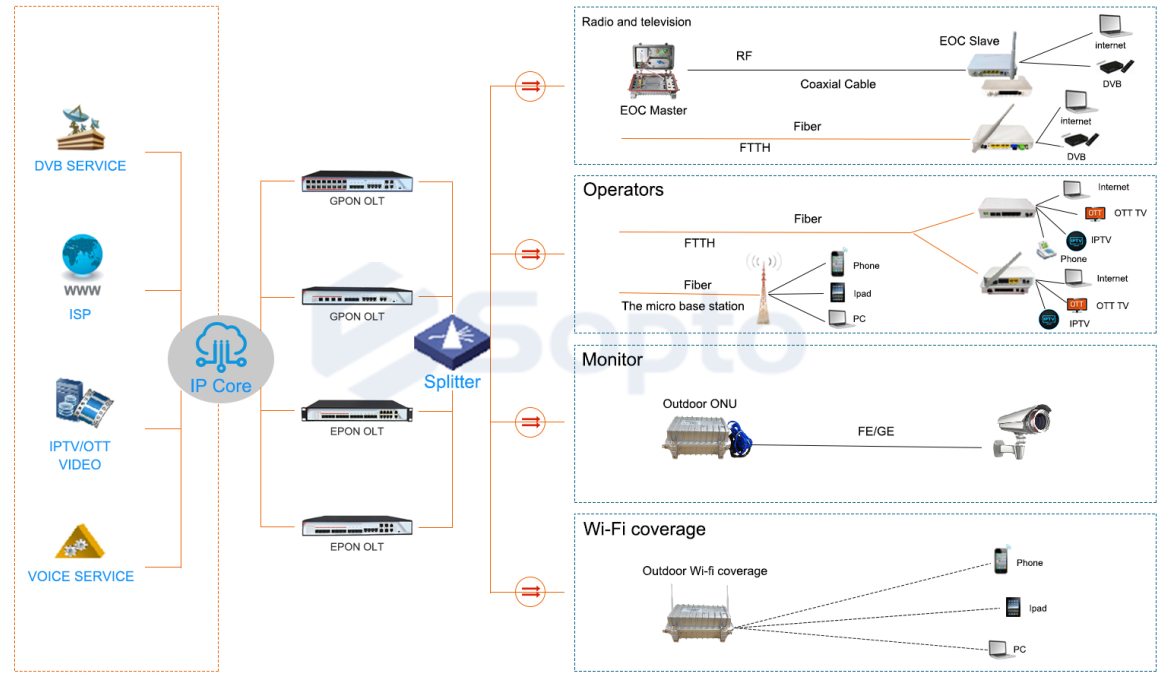
GPON OLT and ONT in Broadband Networks
In broadband networks, GPON OLT and ONT are connected through a passive optical network, providing high-speed internet access and other services to end users.
· High Bandwidth: GPON technology supports downstream rates up to 2.5Gbps and upstream rates up to 1.25Gbps.
· Long-distance Coverage: It supports coverage over distances of more than 20 kilometers.
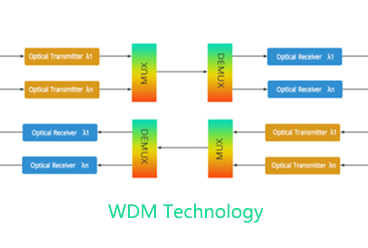
· Efficient Bandwidth Allocation: Through TDM (Time Division Multiplexing) and WDM (Wavelength Division Multiplexing) technologies, it achieves efficient bandwidth allocation and utilization.
· Multi-service Support: Provides various services such as internet, IPTV, and VoIP.
GPON OLT and ONT Deployment
Deployment Process
1. Planning and Design: Determine the coverage area and user requirements, and design the PON network topology.
2. Fiber Installation: Lay the fiber from the OLT to the user end and install optical splitters at appropriate locations.
3. OLT Installation: Install the OLT equipment in the central office, connect the uplink and power, and configure the device.
4. ONT Installation: Install the ONT equipment at the user end, connecting the fiber and user devices.
5. Testing and Debugging: Ensure all connections are normal, perform signal tests, and optimize network performance.
6. User Access: Configure user accounts and services to ensure users can access network services properly.
Considerations
· Fiber Quality: Ensure the quality of fibers and connectors to reduce signal loss and failure rates.
· Equipment Compatibility: Ensure compatibility between OLT and ONT devices to avoid connection issues.
· Network Security: Configure appropriate security measures to prevent unauthorized access and attacks.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What is GPON?
A: GPON stands for Gigabit Passive Optical Network, a fiber optic technology that delivers data, voice, and video services to end users over a single fiber.
Q: What is an OLT in a GPON network?
A: OLT stands for Optical Line Terminal. It is the central device in a GPON network that manages and controls the entire network. The OLT connects to the Optical Distribution Network (ODN) and allocates different types of data and voice traffic from users to the appropriate destinations.
Q: What is an ONT in a GPON network?
A: ONT stands for Optical Network Terminal. It is the device located at the customer's premises that connects to the OLT via the ODN. The ONT module on the ODN receives and transmits data and voice signals between the end-user devices and the GPON network.
Q: What are the roles of an OLT in a GPON network?
A: The main functions of an OLT in a GPON network are:
· Managing and controlling the entire network.
· Allocating different types of data and voice traffic from users.
· Dynamic bandwidth allocation to ensure efficient use of network resources.
· Supporting various services such as VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol) and video streaming.
Q: What are the roles of an ONT in a GPON network?
A: The main functions of an ONT in a GPON network are:
· Receiving and transmitting data and voice signals between the end-user devices and the GPON network.
· Converting optical signals to electrical signals compatible with customer devices.
· Providing interfaces for connecting customer devices such as computers, phones, and televisions to the GPON network.
Q: What is the difference between GPON and EPON?
A: GPON and EPON are both PON (Passive Optical Network) technologies but follow different underlying standards. GPON adheres to the ITU-T G.984 standard, while EPON follows the IEEE 802.3ah standard. GPON is known for its higher bandwidth and wider coverage, while EPON is more cost-effective and has a simpler architecture.
Q: What is Dynamic Bandwidth Allocation in GPON?
A: Dynamic Bandwidth Allocation in GPON is a mechanism that allows the OLT to allocate available bandwidth based on the current demands of the ONTs. By dynamically adjusting the bandwidth allocated to different ONTs according to their traffic needs, it ensures efficient utilization of network resources.
Q: What is the GPON standard?
A: The GPON standard is the ITU-T G.984 standard, which defines the specifications for passive optical networks using Gigabit PON technology. It outlines the protocols and interfaces required for transmitting data, voice, and video over a GPON network.
Q: What is the significance of GPON in fiber optic networks?
A: GPON plays a crucial role in fiber optic networks by providing a cost-effective solution for delivering high-speed broadband services to end users. It can transmit large amounts of data and support various services such as internet access, VoIP, and video streaming. GPON also supports flexible network scalability and future-proofing.
Q: What are the advantages of GPON over traditional copper networks?
A: Some advantages of GPON over traditional copper networks include:
· Higher bandwidth capacity for faster and more reliable internet speeds.
· Longer coverage range, allowing service to a larger coverage area.
· Lower maintenance and operational costs due to the use of passive optical components.
· Ability to deliver multiple services (data, voice, video) over a single fiber connection.
Q: What modules are used for GPON OLT PON ports, GE optical ports, and XGE ports?
A: GE optical ports use standard 1G SFP optical modules, XGE optical ports use standard 10G SFP+ optical modules, and the distance depends on the customer's actual application. My company's GPON modules specifications are:
Average Optical Output Power:
B+: +1.5 to +5dBm
C+: +3 to +8dBm
C++: +4 to +10dBm
Sensitivity:
B+: -28dBm
C+/C++: -30dBm
Saturation:
B+: -8dBm
C+/C++: -10dBm
Q: Can our GPON OLT be connected to ONUs from other brands, such as Huawei and ZTE?
A: GPON OLTs follow the ITU-T G.984 standard, and ONUs from other brands also adhere to this standard without involving proprietary protocols. Therefore, they are generally compatible.
Q: How many GPON ONUs can each PON port of a GPON OLT support?
A: Theoretically, GPON supports a 1:128 split ratio. It is recommended to have fewer than 128 users per PON port, mainly considering future user bandwidth upgrades and the potential impact of faults on a single PON port. A single PON port on a GPON OLT has a maximum downstream rate of 2.5Gbps.
If you would like to learn more about the details of GPON OLT and ONT, please feel free to contact us at any time. Our email is [email protected].
Tags : GPON OLT, GPON ONT, FTTH
— END —