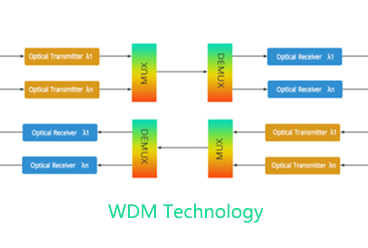
1. Light and its characteristics
Light is an electromagnetic wave. The visible light partial wavelength range is 390-760 nm. The portion larger than 760 nm is infrared light, and the portion smaller than 390 nm is ultraviolet light. The applications in the fiber are 850 nm,1300 nm and 1550 nm.
2. Optical Fiber structure
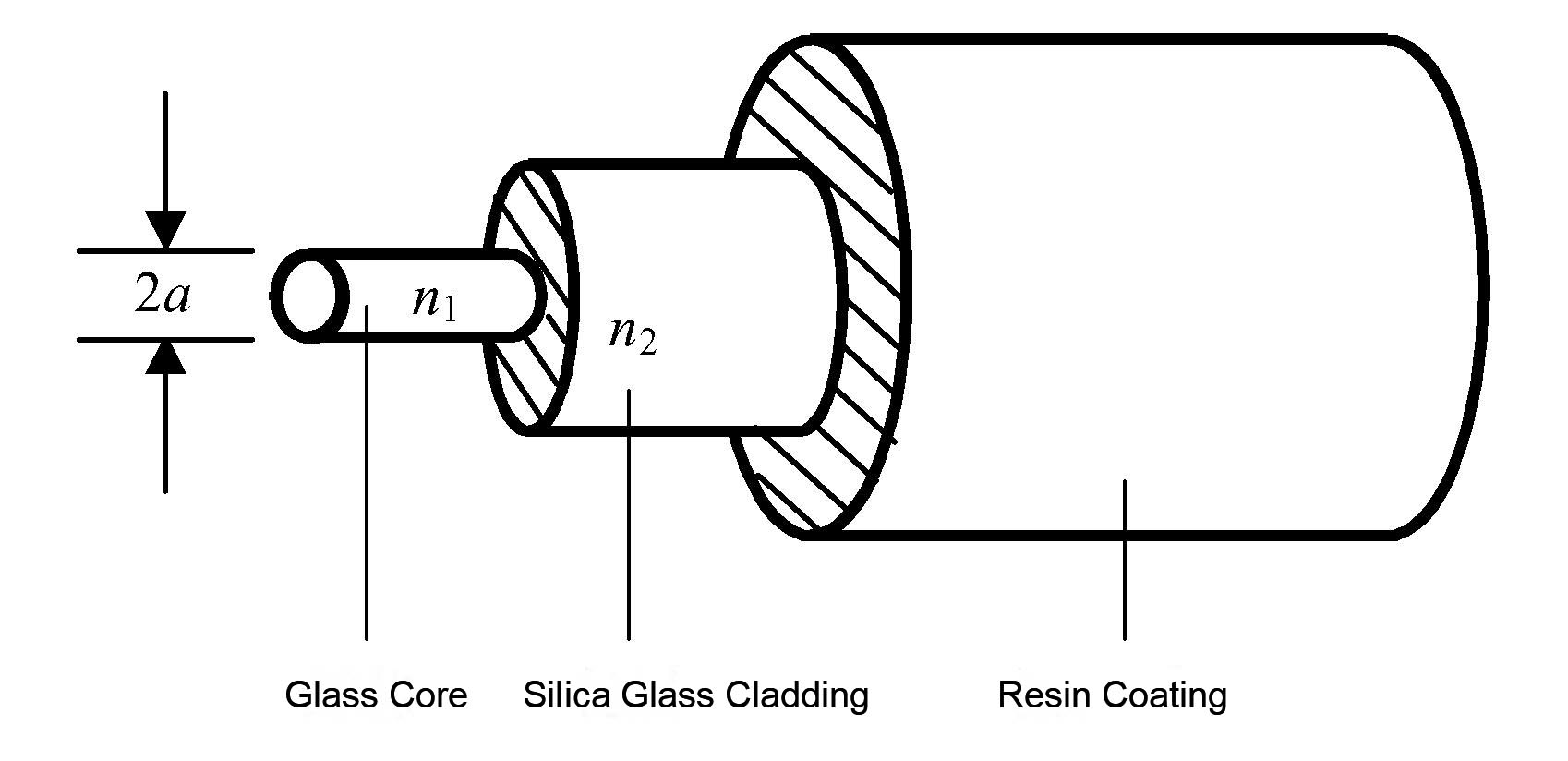
Optical Fiber is a transparent medium fiber used for guiding light. A practical fiber is composed of a plurality of transparent media. The bare fiber is generally divided into three layers, a central high refractive index glass core (core diameter is generally 50 or 62.5). Μm),in the middle is a low refractive index silica glass cladding (typically 125μm in diameter), the outermost is a resin coating for reinforcement.
3.Optical Fiber type
3.1 Classification by transmission mode of light in fiber
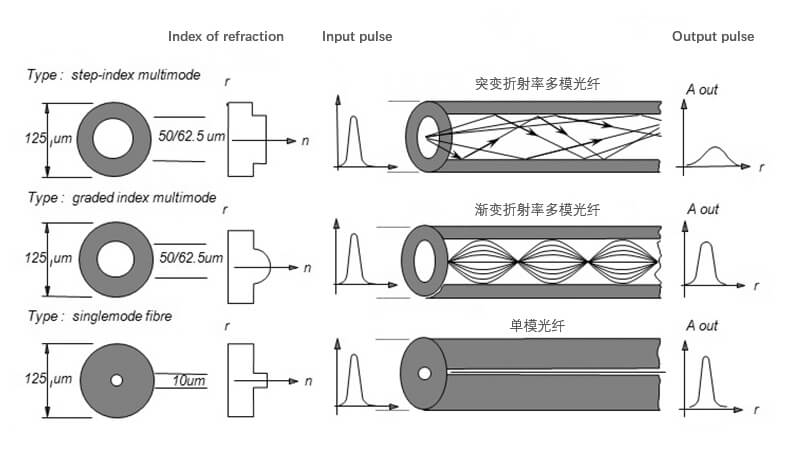
Optical fibers are classified into single-mode fibers and multimode fibers according to the transmission mode of light in the optical fiber.
Multimode fiber: The center glass core is thicker (50 or 62.5 μm) and can transmit multiple modes of light. However, the dispersion between the modes is large, which limits the frequency at which digital signals are transmitted, and is more severe as the distance increases. For example, a 600MB/KM fiber has a bandwidth of only 300MB at 2KM. Therefore, the distance traveled by multimode fiber is relatively close, usually only a few kilometers.
Single mode fiber: The center glass core is thin (the core diameter is generally 9 or 10 μm), and only one mode of light can be transmitted. Therefore, the inter-mode dispersion is small, suitable for remote communication, but its chromatic dispersion plays a major role, so that single-mode fiber has higher requirements on the spectral width and stability of the light source, that is, the spectral width is narrower and the stability is better.
3.2 Classification by refractive index distribution on fiber cross section
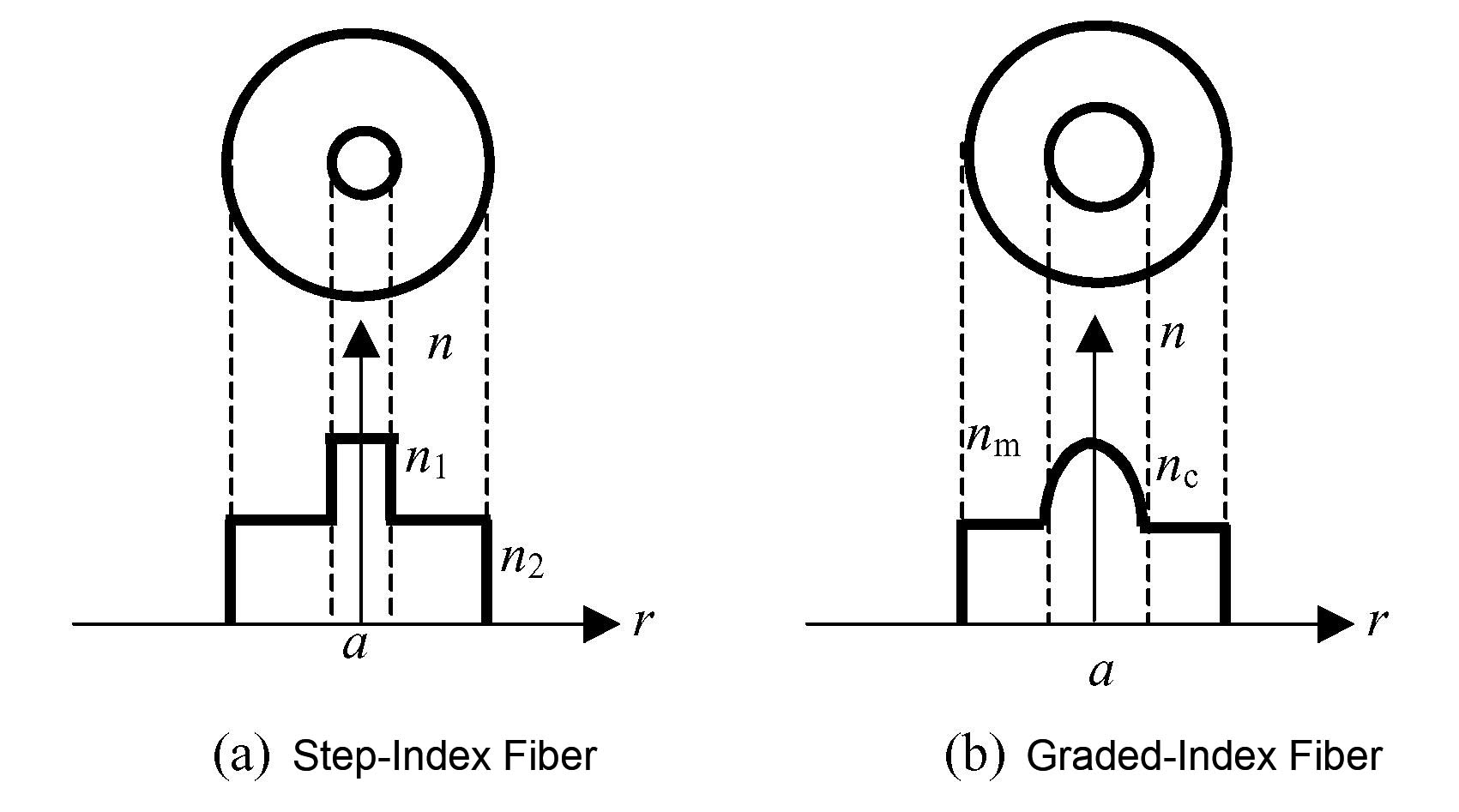
The fiber can be divided into Step-Index Fiber (SIF) and Graded-Index Fiber (GIF) according to the difference in refractive index profile on the cross section.
3.3 Classification according to ITU-T recommendations for fiber types
Fibers can be classified into G.651 fiber (gradient multimode fiber), G.652 fiber (conventional single mode fiber), G.653 fiber (dispersion-shifted fiber), G according to ITU-T recommendations for fiber type classification. .654 fiber (cutoff wavelength fiber) and G.655 (non-zero dispersion shifted fiber) fiber. Among them, G.652 and G.655 are widely used in current projects. G.652, also known as conventional single fiber, can operate at dual wavelengths with minimal dispersion at 1310 nM, with a typical attenuation of 0.34 dB/km. At 1550, the attenuation is at least 0.2 dB/km. G.652 fiber is relatively low in price and mature in technology. It is currently the largest fiber used, accounting for more than 90%.
4.Common fiber specifications
Single mode: 8/125μm, 9/125μm, 10/125μm
Multimode: 50/125μm European standard
62.5/125μm American Standard
Industrial, medical and low speed networks: 100/140μm, 200/230μm
Plastic: 98/1000μm for automotive control.
5.Advantages of fiber
1) The pass band of the fiber is very wide, the theory can reach 3 billion megahertz.
2) No relay section length. From tens to more than 100 kilometers, the copper wire is only a few hundred meters.
3) Not affected by electromagnetic fields and electromagnetic radiation.
4) Light weight and small size. For example: 900 pairs of twisted pairs with 21,000 channels, 3 inches in diameter and 8 tons / KM. The cable with ten times the communication capacity is 0.5 inches in diameter and weighs 450 P/KM.
5) Optical fiber communication is not charged, and it can be used for flammable and explosive places.
6) The ambient temperature range is wide.
7) Chemical corrosion, long service life.
Tags : fiber optical cable
— END —