WDM (Wavelength Division Multiplexing) combines two or more optical carrier signals of different wavelengths (carrying various information) at the transmitting end through a multiplexer (also known as a multiplexer), and The technology of transmitting in the same optical fiber coupled to the optical line. At the receiving end, the optical carrier of various wavelengths is separated by a demultiplexer (also called a demultiplexer or demultiplexer), and then the optical carrier is The receiver performs further processing to restore the original signal. This technology of simultaneously transmitting two or more optical signals of different wavelengths in the same optical fiber is called wavelength division multiplexing.
In the traditional transmission mode, an optical fiber can only transmit optical carrier signals that carry one type of information. If it is for different services, countless different and independent optical fibers are needed for transmission. However, if the amount of business information is large, a large number of optical fibers need to be laid for transmission, which poses a great challenge to wiring space and cost. The application of a WDM system can quickly solve the above problems. It is a technology that uses multiple lasers to simultaneously send multiple lasers of different wavelengths on a single fiber. Each signal is transmitted in its unique color band after being modulated by data (text, voice, video, etc.). WDM can greatly increase the capacity of the existing optical fiber infrastructure of telephone companies and other operators. The WDM system can carry multiple formats of "service" signals, such as ATM, IP, etc., through multiplexing and demultiplexing technology, the multiple service signals can be transmitted through a single optical fiber, which greatly reduces the amount of optical fiber. Ideal means of expansion in expansion and development. When introducing new broadband services, such as CATV, HDTV, B-ISDN, etc., only one additional wavelength needs to be added.
Basic structure of general WDM system
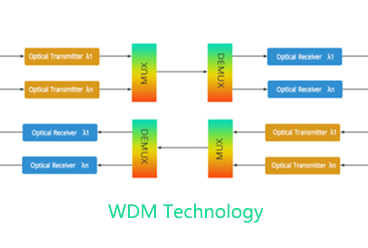
The basic structure of the WDM system is mainly divided into two modes, dual-fiber unidirectional transmission and single-fiber bidirectional transmission. Dual-fiber unidirectional means that all optical paths are transmitted in the same direction on an optical fiber at the same time, and different wavelengths carry different optical signals, which are combined at the transmitting end for transmission through an optical fiber, and demultiplexed at the receiving end to complete multiple paths. The transmission of optical signals is transmitted through another optical fiber in the opposite direction. The transmission in the two directions is completed by two optical fibers respectively. Single-fiber bidirectional means that the optical path transmits in two different directions simultaneously on one optical fiber, and the wavelengths used are separated from each other to achieve full-duplex communication between the two parties.
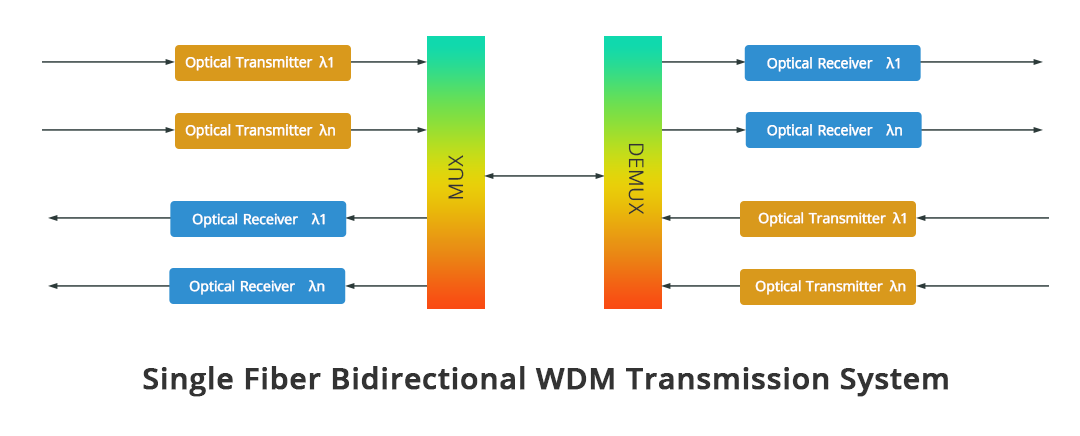
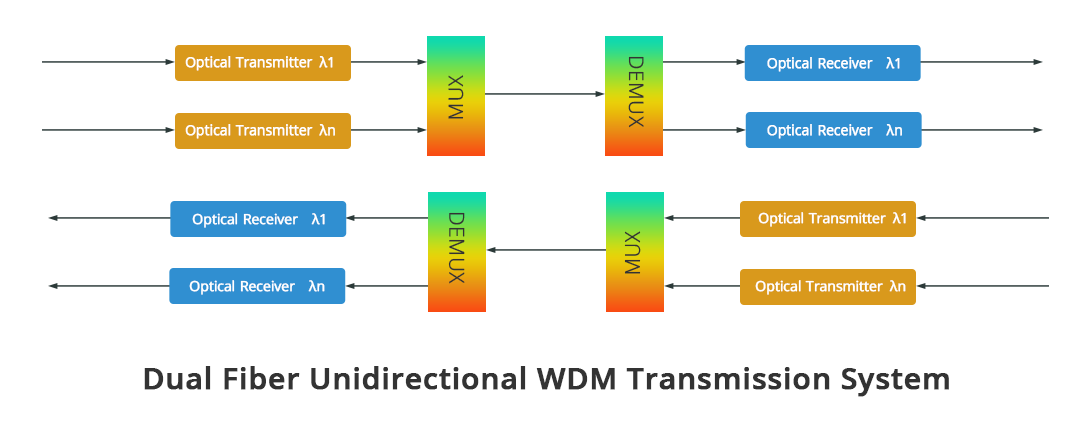
The general WDM system is mainly composed of five parts, Network Management System, Optical Transmitter, Optical Relay Amplifier, Optical Receiver, and Optical Monitoring Channel.
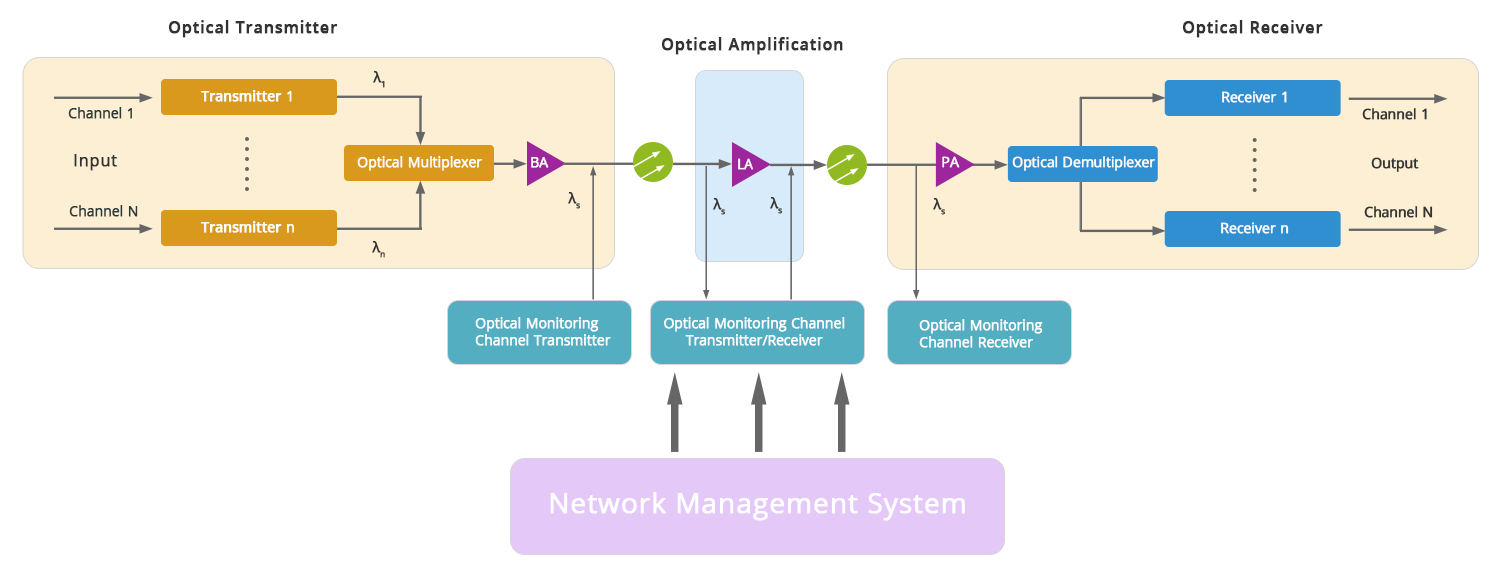
Schematic diagram of the overall structure of the WDM system
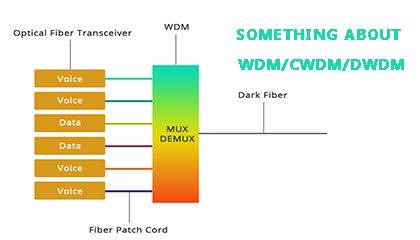
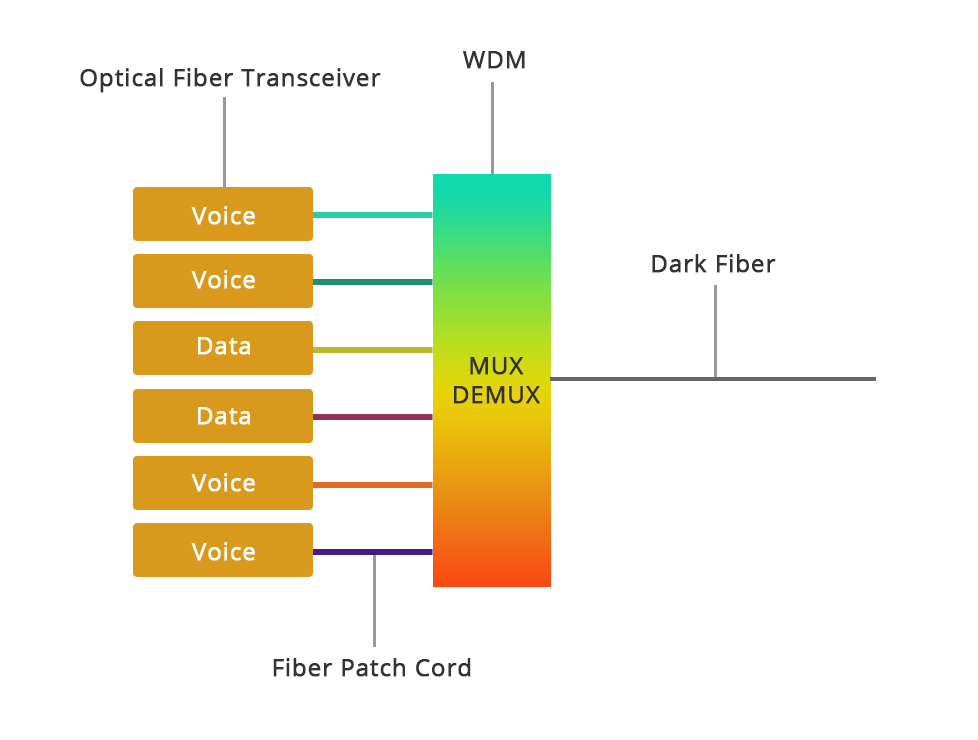
Among them, the simple WDM system mainly includes Optical Fiber Transceivers, WDM Wavelength Division Multiplexers, Fiber Patch Cord, and Dark Fiber Components.
In the entire WDM system, the optical wavelength division multiplexer and demultiplexer are key components in the WDM technology, and their performance is decisive for the transmission quality of the system.
Advantages of WDM wavelength division multiplexing
Large capacity
An important feature of WDM is that it can make full use of the bandwidth resources of the optical fiber and increase the data transmission capacity without changing the existing network infrastructure, so that the transmission capacity of an optical fiber is multiple times that of a single wavelength. The DWDM system can support up to 192 wavelengths of the pair of the optical fiber, the transmission capacity per wavelength up to 100Gbit / s ~ about 400Gbit / s and a Terabit / s.
Good compatibility
WDM has good compatibility with different signals. When signals of different properties such as images, data and voice are transmitted in the same optical fiber, each wavelength is independent of each other and does not interfere with each other, ensuring the transparency of transmission.
High network flexibility, economy and reliability
Wavelength division multiplexing technology allows new channels to be connected as needed without interrupting existing traffic services, making upgrades easier. When upgrading and expanding the network, there is no need to renovate the optical cable line, and new businesses can be opened or superimposed by adding wavelengths, saving a large number of optical fibers and 3R regenerators during large-capacity long-distance transmission, and the transmission cost is significantly reduced.
Wavelength routing
WDM technology is one of the key technologies to realize all-optical networks. In the all-optical network that is expected to be realized in the future, by changing and adjusting the wavelength of the optical signal on the optical path, the up/down and cross-connection of various telecommunication services can be realized.
What is Mux and Demux ?
Multiplexer, MUX
The main function of the multiplexer MUX is to combine multiple signal wavelengths in one optical fiber for transmission. At the transmitting end, N optical transmitters work on N different wavelengths, and these N wavelengths are separated by appropriate intervals, which are respectively denoted as λ1, λ2...λn. These N light waves are respectively modulated by signals as carrier waves to carry signals. A multiplexer combines these optical carrier signals of different wavelengths and couples them into a single-mode fiber. Since the optical carrier signals of different wavelengths can be regarded as independent of each other (when fiber nonlinearity is not considered), multiple optical signals can be multiplexed and transmitted in one fiber. Through multiplexing, communication operators can avoid maintaining multiple lines, effectively saving operating costs.
Demultiplexer, DEMUX
The main function of the demultiplexer DEMUX is to separate multiple wavelength signals transmitted in an optical fiber. In the receiving part, a demultiplexer separates the optical carrier signals of different wavelengths, and the optical receiver performs further processing to restore the original signal. The multiplexer (Demux) is a device that reversely processes the multiplexer.
In principle, the device is reciprocal (two-way reversible), that is, as long as the output and input of the demultiplexer are used in reverse, it is a multiplexer.
What is CWDM, DWDM?
CWDM(Coarse Wavelength Division Multiplexer)
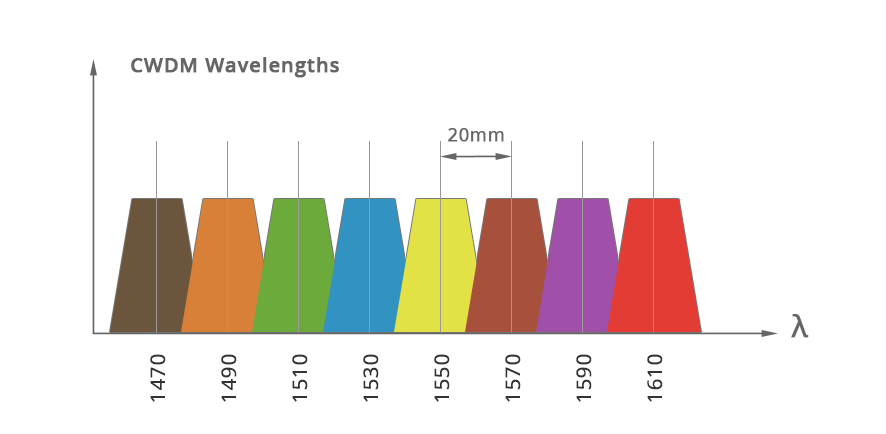
CWDM (Coarse Wavelength Division Multiplexer) is a sparse wavelength division multiplexer, also known as a coarse wavelength division multiplexer. CWDM has 18 different wavelength channels, and the different wavelengths of each channel are separated by 20 nm, and wavelengths from 1270 nm to 1610 nm are used. CWDM supports fewer channels than DWDM because it is compact and cost-effective, making it an ideal solution for short-distance communications. The biggest advantage of the CWDM system is its low cost. The cost of the device is mainly reflected in filters and lasers. The wide wavelength interval of 20nm also brings CWDM the advantages of low requirements on the technical indicators of the laser and the simplified structure of the optical multiplexer/demultiplexer. The structure is simplified and the yield is improved, so the cost is reduced.
DWDM(Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexer)
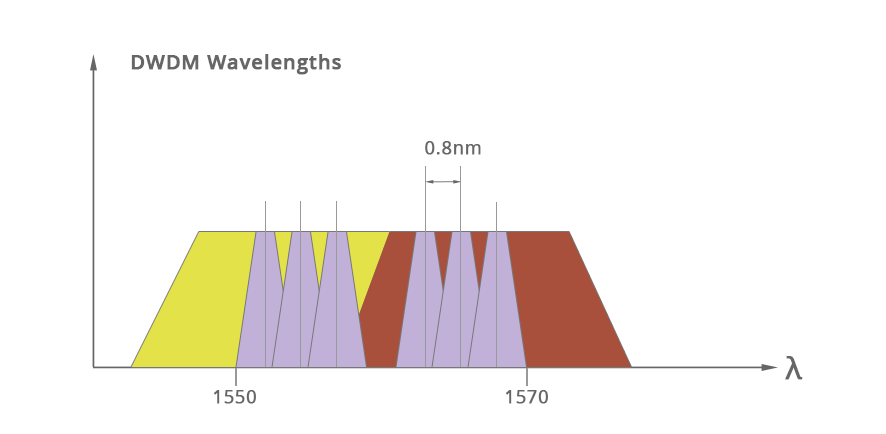
DWDM (Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexer) is a dense wavelength division multiplexer. The channel spacing of DWDM is 1.6/0.8/0.4 nm (200GHz/100 GHz/50 GHz), which is far smaller than CWDM. Compared with CWDM, DWDM with tighter wavelength spacing can carry 8 to 160 wavelengths on an optical fiber, which is more suitable for long-distance transmission. With the help of EDFA, DWDM system can work within thousands of kilometers.
Tags : WDM,CWDM,DWDM,MUX,DEMUX,optical fiber
— END —