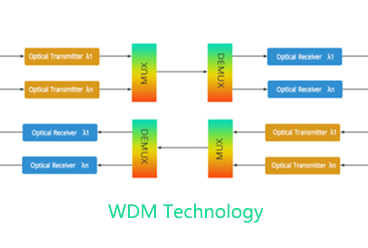
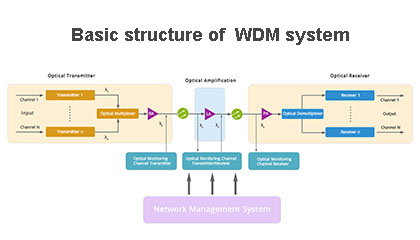
What is a WDM?
WDM stands for Wavelength Division Multiplexer. In fiber-optic communications, wavelength-division multiplexing is a technology which multiplexes a number of optical carrier signals onto a single optical fiber by using different wavelengths (i.e. colors) of laser light.This technique enables bidirectional communications over one strand of fiber, as well as multiplication of capacity. This is done by using light wavelength filters. The filters only allow specific wavelengths of light to pass through the filter to a fiber port and the remainder of the wavelengths to be reflected back to another fiber port. The wavelengths used are defined by the International Telecommunications Union; reference ITU G.694.2 for the ITU WDM Wavelength Grid. 1270nm through 1610nm are the typical wavelengths used in fiber optic communications.
What is a WDM used for?
Fiber Optic WDM’s are used to increase the amount of information or systems that can be transmitted over a single fiber. They are also used to create virtual fiber or fiber relief freeing up existing fibers to be used for other networks or systems.For example a typical 2 channel WDM point to point network will use a 2 channel 1310nm/1550nm multiplexer to combine the two different wavelengths onto one fiber and a demultiplexer at the opposite end to individually demultiplex or separate those wavelengths.This allows you to simultaneously transmit two different signals/systems over the same fiber. This would free up 1 other fiber creating virtual fiber or fiber relief.
What is a CWDM?
CWDM stands for Course Wavelength Division Multiplexer. CWDM’s work similar to the WDM’s explained in questions 1 and 2. “Course” meaning the channel spacing is 20nm with a working channel passband of +/-6.5nm from the wavelengths center. This is tighter channel spacing than typical Wide Band Optic (WBO) WDM’s, which allows for more channels within the ITU CWDM grid. CWDM’s allow you to multiplex or demultiplex multiple wavelengths over one fiber. This is done by using light wavelength filters.The filters only allow specific wavelengths of light to pass through the filter to a single fiber port and the remainder of the wavelengths are then reflected back to another separate fiber port. When used in a series or concatenated together this allows you to add multiple wavelengths on to one fiber. From 1270nm to 1610nm there are 18 individual wavelengths/channels separated by 20nm spacing.
What is a CWDM used for?
Fiber Optic CWDM’s are used to increase the amount of information or systems that can be transmitted over a single fiber. They are also used to create virtual fiber or fiber relief freeing up existing fibers to be used for other networks or systems.For example a typical 4 channel CWDM point to point network will use a multiplexer to combine four different wavelengths onto one fiber and a demultiplexer at the opposite end to individually demultiplex or separate the wavelengths. This allows you to simultaneously transmit four different signals/systems over the same fiber. This would free up 3 other fibers on a four fiber network creating virtual fiber or fiber relief.
What is a DWDM?
DWDM stands for Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexer. DWDM’s allow you to multiplex or demultiplex more than one wavelength over one fiber similar to the CWDM mentioned in questions 3 and 4. The word “Dense” is referring to the very narrow channel spacing measured in Gigahertz (GHz) as opposed to nanometer (nm).DWDM’s typically use channel spacing of 100GHz with a working channel passband of +/-12.5GHz from the wavelengths center. This allows you to add multiple wavelengths on to one fiber within the 1550nm band which are wavelengths between approximately 1525nm–1565nm (C band) and/or 1565nm–1625nm (L band) adhering to the DWDM ITU-T G.694.1 frequency grid. DWDM’s will also use 200GHz spacing essentially skipping every other channel in the DWDM grid. They have also gone one step further using an Optical Interleaver to get down to 50GHz spacing doubling the channels capacity from 100GHz spacing.
What is a DWDM used for?
Similar to CWDM’s mentioned in questions 3 and 4 DWDM’s are used to increase the amount of information or systems that can be transmitted over a single fiber. The DWDM’s will allow for many more channels using much tighter channel spacing. Typical DWDM’s will allow for but not limited to 32, 40 and 44 channels, while the 50GHz spacing will double that and allow for 64, 80 and 88 channels.
What is an OADM?
OADM stands for Optical Add Drop Multiplexing. This module is used to Add and Drop specific wavelengths while letting all other wavelengths continue to pass through. A typical OADM is a 4 port module that has East and West Common ports and a Drop port and Add Port. The first common port typically referred to as the East port will receive all of the wavelengths being transmitted through the single fiber. Using a filtered component it will then separate and drop one wavelength to the 2nd port, then allow the same wavelength to be transmitted on the 3rd port adding it to continue through the West Common port.
How many channels are available for CWDM and DWDM?
Clearfield follows the standard ITU-T G694.2 for WDM/CWDM using the wavelengths 1270nm to 1610nm which gives us 18 CWDM wavelengths. Clearfield has also added 1630nm and 1650nm wavelengths that are used for live testing in newer model OTDR’s. For the DWDM channels Clearfield follows the ITU-T G.694.1 Grid. Today's DWDM systems using 100GHz, 50GHz or even 25GHz channel spacing can get up to 160 channels of operation.
Does your CWDM/OADM accommodate OC-3/12/48/192, GigE, 10 GigE optical signals?
The Clearfield passive optical components will accommodate OC-3/12/48/192, GigE, 10 GigE optical signals. The Passive Optical Components are typically not the limiting factor to what type of network or speed that can be run through it. This limiting factors are determined by the types of transmitters and receivers used in the network along with the quality of the fiber optic network being used.
What is the maximum fiber distance per fiber span when deploying CWDM/DWDM/Circulators?
The maximum fiber distance is not determined by the optical component. Like any other fiber network the distance a signal can go is based on the output power of the laser/transmitter and the overall link loss acceptable for the equipment/receiver being used.
Tags : WDM , CWDM , DWDM , Fiber WDM, WDM OADM
— END —