
- Media Converter
- 10/100M Media Converter 10/100/1000M Media Converter 10G Media Converter Multi UTP Fiber Media Converter Multi UTP POE Fiber Media Converter Industrial Fiber Media converter Point to point Manageable Fiber Media Converter OEO Converter 14 Slots Media Converter Chassis 16 Slots Media Converter Chassis Mini Media Converter
- Fiber Patch Cords
- Fiber Pigtails FTTH Drop Patch Cords CPRI Patch Cords MPO Patch Cords Fiber Optic Patch Cords
- Fiber Terminal Box
- 96 cores Fiber Terminal Box 72 cores Fiber Terminal Box 48 cores Fiber Terminal Box 24 cores Fiber Terminal Box 12 cores Fiber Terminal Box 8 cores Fiber Terminal Box 4 cores Fiber Terminal Box 2 cores Fiber Terminal Box 1 core Fiber Terminal Box
- Indoor Distribution Frame
- 1800 cores Indoor Distribution Frame 1440 cores Indoor Distribution Frame 720 cores Indoor Distribution Frame 576 cores Open Rack 576 cores Indoor Distribution Frame 288 cores Indoor Distribution Frame
- Outdoor optical cabinet
- 576 cores Outdoor Optical Cabinet 288 cores Outdoor Optical Cabinet 144 cores Outdoor Optical Cabinet 96 cores Outdoor Optical Cabinet
- Fiber Patch Panel
- 19-inch 3U Splitter Rack 96 cores-144 cores FDU 96 cores Fiber Patch Panel 72 cores Fiber Patch Panel 48 cores Fiber Patch Panel 36 cores Fiber Patch Panel 24 cores Fiber Patch Panel 12 cores Fiber Patch Panel 12cores-96cores ODF Unit Box
- Splitter Distribution Box
- 72 cores Splitter Distribution Box 48 cores Splitter Distribution Box 36 cores Splitter Distribution Box 32 cores Splitter Distribution Box 24 cores Splitter Distribution Box 16 cores Splitter Distribution Box 12 cores Splitter Distribution Box 8 cores Splitter Distribution Box 6 cores Splitter Distribution Box 4 cores Splitter Distribution Box 2 cores Splitter Distribution Box
- Fiber Optical Test
- OTDR Launch Cable Box OTDR PON Optical Power Meter Optical Power Meter Optical Variable Attenuator Optical Fiber Identifier Optical Light Source Visual Fault Locator

Data Center Solutions Construction and operation of data center will break the distributed construction mode. High centralized management of dynamic use of physical resources and virtual resources ...

FTTx Solutions Along with the fast deployment of FTTX and its worldwide application. Sopto Technology offers an end-to-end infrastructure solution for central office (CO), optical distribution...

LTE Solutions In telecommunication, Long-Term Evolution (LTE) is a standard for high-speed wireless communication for mobile devices and data terminals, based on the GSM/EDGE and...

10G SFP Transceiver Series Sopto provides a series of 10G transceiver modules, including SFP+, XFP, BIDI SFP+, BIDI XFP, CWDM/DWDM SFP+; They are designed for using in 10G Ethernet, 10G Fiber Channel, SONET/SDH OC-192/STM-64, and OTN OTU2e links. Digital diagnostics functions. RoHS compliant.

XPON ONU Series ONU of user side provides interface for services like data, internet video, CATV and VOIP, wifi. By applying Ethernet, GEM protocol and so on, to implement transparent transmission of user data in PON system.
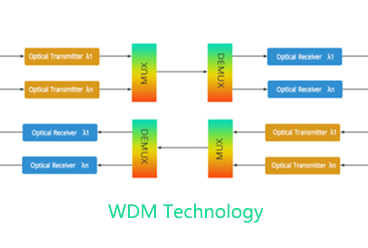
WDM Networking Solution WDM (Wavelength Division Multiplexing) technology was developed to expand capacity of networks. WDM system uses a Multiplexer at the transmitter to combine several wavelengths together, each one carry different signal with bite-rate up to 10G and a demultiplexer at the receiver to split them apart.

SFP+ MPO Cable On Sale As a manufacturer of optical modules for data centers,sopto offers optical modules with different data rate to meet the different needs of our customers, and we also accept customized services. All optical transceivers are RoHS compliant and could be 100% compatible with branding equipment, such as Cisco, Extreme, Juniper, HP, H3C, Linksys etc
SFP Module On Sale As a manufacturer of optical modules for data centers,sopto offers optical modules with different data rate to meet the different needs of our customers, and we also accept customized services. All optical transceivers are RoHS compliant and could be 100% compatible with branding equipment, such as Cisco, Extreme, Juniper, HP, H3C, Linksys etcPart No.DescriptionPriceDetailsSPT-P131G-10D/20D1.25G 1310nm 10/20km DDM SFP$3.85/PCPDFSPT-PB351G-L20D1.25G 1310nm 20km DDM SFP $4.2/PCPDFSPT-PB531G-L20D1.

SFP Module Transceivers Sopto provides standardized transceivers Modules and customized transceivers Modules for data-rate of 1-100G network. Types of Dual fiber/ Single fiber and wavelengths of 850nm/ 1310nm/ 1490nm/ 1550nm/ CWDM 1270 - 1610nm/ DWDM wavelengths and transmitting distance from 30m up to 150km can be selected. Digital Diagnostic Function are also available. All optical transceivers Modules are RoHS compliant and could be 100% compatible with branding equipment, such as Cisco, Extreme, Juniper, HP etc.

Fiber Optic Cable Fiber Optic Cable, also known as an optical fiber cable, is an assembly similar to an electrical cable, but containing one or more optical fibers that are used to carry light. The optical fiber elements are typically individually coated with plastic layers and contained in a protective tube suitable for the environment where the cable will be deployed. Different types of cable are used for different applications, for example long distance telecommunication, or providing a high-speed data connect
Fiber Optic Patch Cords Fiber patch cords are used to connect one device to another for signal transmission. The fiber jumper is a connector that is installed at both ends for the device; only one end is equipped with a connector, which is a pigtail. Depending on the type of fiber, there are single mode jumpers and multimode jumpers. According to the structure of the connector, it can be divided into FC, SC, ST, LC, MTRJ, MPO, MU, E2000, DIN, and the like.

GPON ONU Dual WIFI For 2.4G & 5G Now 5g construction has set off a wave of enthusiasm, 5G networks have significant improvements in throughput, latency and number of conn ections, compared with 4G networks. 5G is the next phase of mobile technology and is widely believed faster, smarter and more efficient than 4G.

ONU 1GE Series GPON is the latest generations of access network technology. ITU-T G.984 is the standard protocol of GPON. EPON is the latest generations of access network technology. IEEE802.3ah is the standard protocol of EPON. PON networks provides the reliability and performance expected for business services and provides an attractive way to deliver residential services. GPON enables Fiber To The Home (FTTH) deployments economically resulting to accelerated growth worldwide










