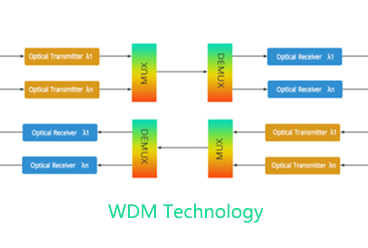
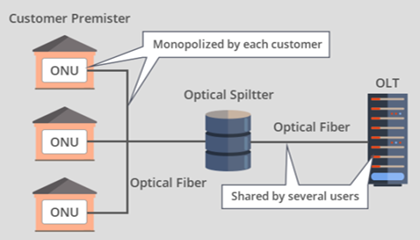
Composition of PON
OLT--Optical Line Terminal
ONU--Optical Network Unit
ONT--Optical Network Terminal
ODN--Optical Distribution Network
The generation and development of passive optical network depend to a large extent on the system structure and topology of PON. Below we will briefly introduce them.
For the PON system structure (passive optical network), it is mainly composed of passive components such as optical fiber, passive optical splitter and wavelength division multiplexer, and does not contain any active components. PON is divided into three parts: optical line terminal OLT, optical distribution network ODN and optical network unit ONU. Among them, the OLT is connected to one or more ODN to provide a network interface for the ODN. ODN provides transmission means for OLT and ONU, and ONU is connected with ODN to provide user-side interface for ODN. Multiple ONU are connected to OLT via ODN and share the optical transmission medium and optoelectronic equipment of OLT, thereby reducing optical access costs.
The PON topology is a point-to-multipoint optical fiber transmission system. The downlink uses broadcast frames and the uplink uses time division multiple access. No node equipment is required at the optical branch point, and only a simple splitter is required. . The topological structure of PON depends on the structure of ODN, which can be mainly divided into 4 topological structures: star topology, bus topology, ring topology, and tree topology.
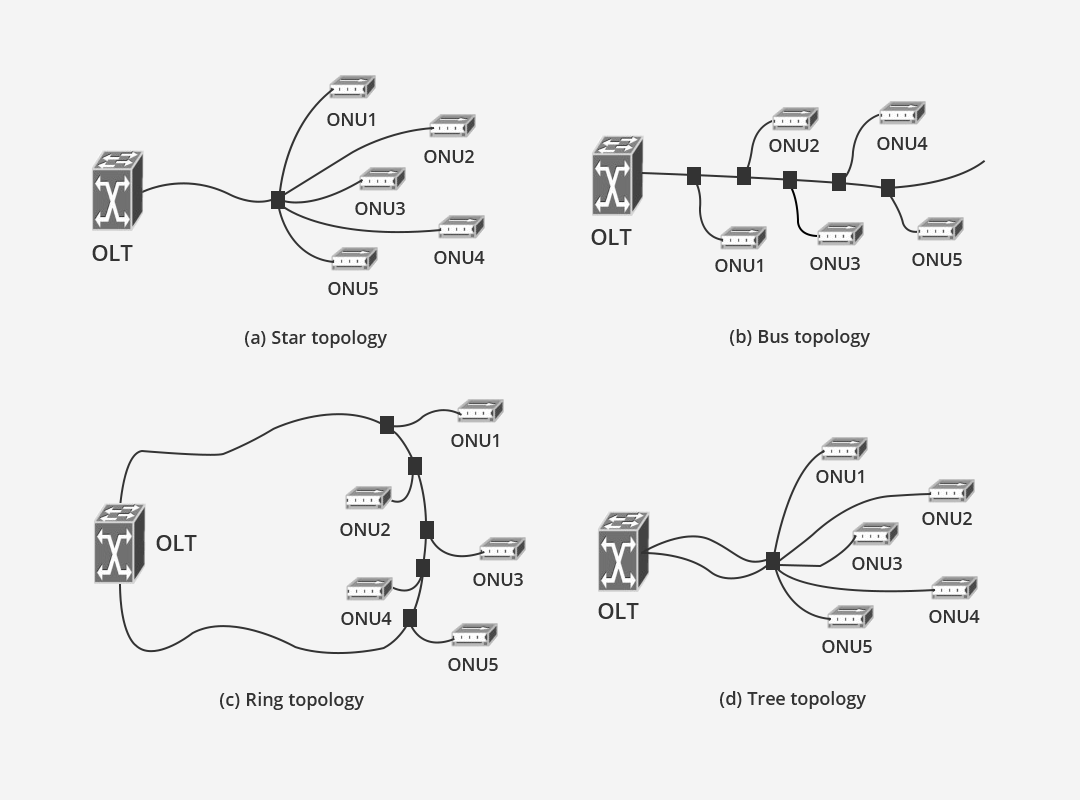
a. Star Topology. The star structure means that each ONU at the user end is connected to the same OLT of the end office through one or a pair of optical fibers to form a star connection structure that radiates around the OLT. The characteristics of this structure are: no optical splitter is used in the optical fiber connection, there is no optical signal attenuation introduced by the splitter, and the network coverage is large; there is no active electronic equipment in the line, and it is a pure passive network. Line maintenance is simple; independent optical fiber channels are used, ONUs do not affect each other and have good confidentiality performance, which is easy to upgrade; but the cost is too high, the amount of optical cables required is large, and optical fibers and light sources cannot be shared.
b. Bus Topology. Bus (Bus) topology PON usually adopts non-uniform light splitting OBD to be arranged along the line. OBD separates the optical signal transmitted by the OLT from the optical bus, and inserts the optical signal from each ONU into the optical bus. Non-uniform optical OBD only introduces a small amount of loss to the bus, and only a small amount of optical power is divided from the optical bus. Due to the loss on the optical fiber line, the strength of the optical signal received near the OLT and far away from the OLT is quite different. Therefore, the dynamic range of the optical receiver in the ONU is required to be higher. This structure is suitable for user environments distributed linearly along streets and highways.
c. Ring Topology. The ring structure is equivalent to a closed loop composed of a bus structure, and its signal transmission method is similar to the device and bus structure used. This kind of ring structure forms a reliable self-healing ring network, so that each OBD can pass to the OLT from two different directions, and the reliability is much better than the bus structure.
d. Tree Topology. In the tree topology of PON (also called multi-star topology), the first optical branching device (OBD) connected to the OLT divides the light into n channels, and each channel leads to the next level of OBD, such as the last The first level OBD also has n channels and connects n ONUs. Therefore, it expands the application range of PON with the requirement of increasing the optical power budget. This structure realizes the transparent transmission of optical signals, easy line maintenance, no lightning and electromagnetic interference, and high reliability; users can share some optical facilities, such as the feeder section and wiring section of the optical cable, and the transmission light source of the central office. However, due to the optical power provided by one light source in the OLT to all ONUs, the optical power of the light source is limited, which limits the number of connected ONUs and the transmission distance of optical signals.
The series OBD used in the PON tree topology has two types: uniform optical splitting and non-uniform optical splitting according to a rated ratio. The network formed by the uniform optical splitting OBD is generally called a multi-star topology, and the network formed by the non-uniform optical splitting OBD is often called a tree topology. For the general access network user distribution environment, these two structures have the widest application range.
Ring topology is not an independent topology, actually a combination of two of the bus structure; and a multi-star topology and star topology, tree topology is a special case. In this way, the four topological structures can be summarized as the two most basic structures of tree type and bus type. The factors to be considered when choosing a PON topology are: user distribution topology, distance between OLT and ONU, optical channels that provide various services, available technologies, optical power budget, wavelength allocation, upgrade requirements, reliability, operation and Maintenance, safety, and cable capacity, etc.
Tags : FTTx , ONU , OLT , PON Network , Fiber Solution
Related Products : GPON OLT , EPON OLT , EPON ONU , GPON ONU
— END —