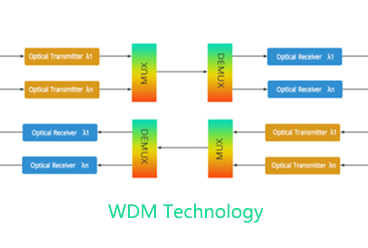
Optical fiber is the abbreviation of optical fiber. It is a kind of fiber made of glass or plastic. It can transmit optical signals thousands of kilometers away, and combine hundreds of thousands of optical fibers to make an optical fiber cable like a cable. Therefore, the optical cable is composed of a certain number of optical fibers with a cable core wrapped with a sheath and a protective layer, which not only improves the strength of the optical fiber, but also greatly increases the communication capacity.
The application of optical fiber cable is extremely wide, and the application scenarios are roughly as follows;
A. Backbone transmission network (SDH/SONET), such as submarine optical fiber cables between major cities and ocean floors;
B. Ethernet, including the current fiber to the home (FTTH), to the building (FTTB), to the community, etc., mainly our home and office networks;
C. Data network (Fiber Channel), various storage devices, databases, including the cloud computing service system under development;
D. Cable TV transmission (PIN reception);
E. Transmission for other special purposes, such as fighter planes and ships.
The following are 43 common questions about fiber optic cables
1. The basic structure of optical fiber
The bare fiber of optical fiber is generally divided into three layers, the center is a high refractive index glass core (the core diameter is generally 50 or 62.5μm), the middle is a low refractive index silica glass cladding (the diameter is generally 125μm), and the outermost is a resin coating for reinforcement. Floor. Optical fiber is short for optical fiber. It is a fiber made of glass or plastic. It can be used as a light transmission tool. The transmission principle is "total reflection of light".
2. What are the basic parameters of optical fiber line transmission characteristics?
Including loss, dispersion, bandwidth, cutoff wavelength, mode field diameter, etc.
3. What are the main factors of fiber attenuation?
The main factors that cause fiber attenuation are: intrinsic, bend, squeeze, magazine, unevenness, and butt, etc.
Intrinsic: It is the inherent loss of optical fiber, including: Rayleigh scattering, inherent absorption, etc.
Bending: When the optical fiber is bent, part of the light in the optical fiber will be lost due to scattering, causing loss.
Squeeze: The loss caused by the slight bending of the optical fiber when it is squeezed.
Impurities: Impurities in the optical fiber absorb and scatter the light propagating in the optical fiber and cause losses.
Non-uniformity: The loss caused by the non-uniform refractive index of the optical fiber material.
Butt joint: the loss caused by fiber butt, such as: different axis (single-mode fiber coaxiality requirement is less than 0.8μm), the end face is not perpendicular to the axis, the end face is not flat, the butt core diameter is not matched, and the splicing quality is poor.
4. How is the attenuation coefficient defined?
Defined by the attenuation per unit length of a uniform fiber in the steady state (dB/km).
5. What is insertion loss?
Refers to the attenuation caused by inserting optical components (such as connectors or couplers) in optical transmission lines.
6. What is the bandwidth of optical fiber related to?
The bandwidth of an optical fiber refers to the modulation frequency when the optical power amplitude is 50% or 3dB lower than the zero frequency amplitude in the transfer function of the optical fiber. The bandwidth of an optical fiber is approximately inversely proportional to its length, and the product of the bandwidth length is a constant.
7. What is the dispersion of optical fiber?
Different frequency components or different mode components of the optical signal (pulse) transmitted in the optical fiber propagate at different speeds, and signal distortion (pulse broadening) will inevitably occur after reaching a certain distance. The generation of fiber dispersion is based on two factors. One is that the optical signal entering the fiber is not monochromatic light (the light emitted by the light source is not monochromatic or the modulated signal has a certain bandwidth); the second is the dispersion effect of the fiber on the optical signal .
8. How to describe the dispersion characteristics of signal propagation in optical fiber?
It can be described by pulse broadening, fiber bandwidth and fiber dispersion coefficient.
9. What is the cut-off wavelength?
It means that a single-mode fiber usually has a certain wavelength. When the transmitted light wavelength exceeds this wavelength, the fiber can only propagate light of one mode (fundamental mode), and under this wavelength, the fiber can propagate multiple modes ( Contains high-order modes) light.
10. What effect does the dispersion of the optical fiber have on the performance of the optical fiber communication system?
The dispersion of the optical fiber will broaden the transmission of light pulses in the optical fiber. Affects bit error rate, transmission distance and system rate.
11. What is backscatter?
Backscatter is a method of measuring attenuation along the length of a fiber. Most of the optical power in the optical fiber propagates forward, but there is also a small amount of optical power scattered to the back of the illuminator. The time curve of backscatter can be observed by using a spectroscope. Starting from one end, not only the length and attenuation of uniform optical fibers can be measured, but also local irregularities, break points and optical power loss at joints and connectors can be measured.
12. What is the testing principle of OTDR? What is the function?
OTDR is made based on the principles of backscattering and Fresnel reflection of light. It uses the backscattered light generated when light propagates in an optical fiber to obtain attenuation information. It can be used to measure the attenuation of the fiber, the loss of the connector, the location of the fiber failure point, and to understand the loss distribution along the length of the fiber. It is an indispensable tool in the construction, maintenance and monitoring of optical cables. Its main parameters include: dynamic range, sensitivity, resolution, measurement time and blind zone.
13. What is the blind zone of OTDR? What is the impact on testing? How to deal with the blind zone in the actual test?
Generally, a series of blind spots caused by saturation of the OTDR receiver are called blind spots.
The blind zone in the optical fiber can be divided into event blind zone and attenuation blind zone: the distance from the beginning of the reflection peak caused by the interference of the active connector to the saturation peak of the receiver is called the event blind zone; from the starting point of the reflection peak to the active connector in the optical fiber The distance of the point at which other events caused by interference can be identified is called the attenuation blind zone.
For OTDR, the smaller the dead zone, the better. As the pulse width increases, the dead zone increases. Although the increase in pulse width increases the measurement length, it also increases the measurement dead zone. Therefore, when testing the optical fiber, the measurement of the OTDR and its adjacent event points by the optical fiber should adopt a narrow pulse, and the measurement of the distal end of the optical fiber should adopt a wide pulse.
14. Can OTDR measure different types of optical fibers?
If you use a single-mode OTDR module to measure a multi-mode fiber, or use a multi-mode OTDR module to measure a single-mode fiber with a core diameter of 62.5 mm, the measurement result of the fiber length will not be affected, but the results such as fiber loss, optical connector loss and return loss Incorrect. Therefore, when measuring optical fibers, it is necessary to select an OTDR matching the optical fiber under test for measurement in order to obtain correct results of various performance indicators.
15. What does "1310nm" or "1550nm" mean in ordinary optical test instruments?
It refers to the wavelength of the optical signal. The wavelength range of optical fiber communication is in the near-infrared region, and the wavelength is between 800nm and 1700nm. It is usually divided into short wave band and long wave band, the former refers to 850nm wavelength, the latter refers to 1310nm and 1550nm wavelength.
16. In the current commercial optical fiber, which wavelength of light has the smallest dispersion? What wavelength has the least light loss?
The wavelength of 1310nm has the smallest light dispersion, and the wavelength of 1550nm has the smallest light loss.
17. How to classify optical fiber according to the change of core refractive index?
Divided into step fiber and gradient fiber. The stepped fiber has a narrow bandwidth and is suitable for small-capacity short-distance communications; the graded fiber has a wide bandwidth and is suitable for large and medium-capacity communications.
18. How to classify optical fibers according to the different modes of light wave transmission in optical fibers?
Divided into single-mode fiber and multi-mode fiber. The core diameter of a single-mode fiber is about 1-10μM. At a given wavelength, only one fundamental mode is transmitted, which is suitable for large-capacity telecommunication systems. Multimode fiber can transmit multimode light waves, and its core diameter is about 50-60μM, and its transmission performance is worse than single-mode fiber.
When transmitting the current differential protection of multi-channel protection, a multi-mode optical fiber is used between the photoelectric conversion device of the communication room of the substation and the protection device of the main control room.
19. What is the meaning of step index fiber numerical aperture (NA)?
The numerical aperture (NA) represents the light-collecting ability of the optical fiber. The larger the NA, the stronger the light-collecting ability of the optical fiber.
20. What is the birefringence of single-mode fiber?
There are two orthogonal polarization modes in a single-mode fiber. When the fiber is not completely cylindrical, the two orthogonal polarization modes do not degenerate. The absolute value of the difference between two orthogonal polarization modes is birefringence.
21. What is the most common fiber optical cable structure?
There are stranded fiber optic cables, beam tube fiber optic cables, skeleton fiber optic cables and ribbon fiber optic cables.
22. What are the main components of fiber optical cable?
It is mainly composed of fiber core, fiber paste, sheath material, polybutylene terephthalate and other materials.
23. What is the armor of the fiber optical cable?
It refers to the protective element (usually steel wire or steel tape) used in special purpose fiber optical cables (such as submarine optical cables, etc.), and the armor is attached to the inner sheath of the fiber optical cable.
24. What material is used for the fiber optical cable sheath?
The fiber optical cable sheath is usually made of polyethylene (PE) and polyvinyl chloride (PVC) materials, and its function is to protect the optical cable core from external influences.
25. List the special fiber optical cables used in the power system.
Overhead fiber optical cables parallel to power lines generally refer to power overhead fiber optical cables. According to the materials used, they can be divided into two categories, metal fiber optical cables and dielectric fiber optical cables. According to the laying form, they can be divided into (power line) multiplexing type (power line), (tower) addition type and (power line) Three types of additional types. They are optical fiber composite ground wire (OPGW), optical fiber composite phase wire (OPPC), metal self-supporting optical cable (MASS), all-dielectric self-supporting optical cable (ADSS), bundled optical cable (ADL) and twisted optical cable (GWWOP). Kind.
26. What is the application structure of OPGW fiber optical cable?
a. Plastic tube layer stranding + aluminum tube structure;
b. Central plastic tube + aluminum tube structure;
c. Aluminum skeleton structure;
d. Spiral aluminum tube structure;
e. Single layer stainless steel tube structure (central stainless steel tube structure, Stainless steel tube layer stranded structure);
f. Composite stainless steel tube structure (central stainless steel tube structure, stainless steel tube layer torsion structure).
27. What are the main components of the stranded wire outside the OPGW fiber optical cable core?
It is composed of AA wire (aluminum alloy wire) and as wire (aluminum clad steel wire).
28. What are the technical conditions for selecting OPGW fiber optical cable models?
a. Nominal tensile strength (RTs) (KN) of OPGW cable,
b. Number of cores of OPGW fiber optical cable (SM),
c. Short-circuit current (KA)
d. Short-circuit time (s),
e. Temperature range (℃) ).
29. How to limit the bending degree of fiber optical cable?
The bending radius of the fiber optic cable is not less than 20 times the outer diameter of the fiber optic cable, and not less than 30 times the outer diameter of the fiber optic cable during the construction process (non-static).
30. What should be paid attention to in ADSS fiber optical cable engineering?
The mechanical design of the fiber optical cable, the determination of the lifting point, and the selection and installation of supporting hardware are three key technologies.
31. What are the main fiber optical cable accessories?
Fiber optical cable hardware refers to the hardware used to install fiber optical cables, mainly including, strain clamps, suspension clamps, shock absorbers, etc.
32. Fiber connectors have two basic performance parameters. what are they?
Fiber connectors are commonly known as flexible connectors. In view of the optical performance requirements of a single fiber connector, the two most basic performance parameters of insertion loss and return loss are focused on.
33. What are the common optical fiber connectors?
According to different classification methods, fiber connectors can be divided into different types. According to the different transmission media, it can be divided into single-mode fiber optic connectors and multi-mode fiber optic connectors. According to the different structure, it can be divided into FC, SC, ST, D4, DIN, biconic, mu, LC, MT and other types. According to the pin end face of the connector, it can be divided into FC, PC (UPC) and APC. Commonly used fiber optic connectors: FC/PC fiber optic connectors, SC fiber optic connectors, LC fiber optic connectors.
34. What is the insertion loss (or insertion loss) of the fiber connector?
Refers to the reduction in the effective power of the transmission line caused by the intervention of the connector. For users, the smaller the value, the better. According to ITU-T, this value should not be greater than 0.5dB.
35. What is the return loss (or reflection attenuation, return loss, return loss) of the fiber connector?
It measures the input power component reflected back from the connector and back along the input channel. Its typical value should not be less than 25dB.
36. What is the most significant difference between the light emitted by an LED and a semiconductor laser?
The light produced by the LED is incoherent light with a broad spectrum, and the light produced by the laser is coherent light with a narrow spectrum.
37. What is the most obvious difference between the operating characteristics of LED and LD?
LED has no threshold, LD has a threshold. Only when the injected current exceeds the threshold will laser light be generated.
38. What are the two commonly used single longitudinal mode semiconductor lasers?
Both DFB lasers and DBR lasers are distributed feedback lasers. Their optical feedback is provided by the distributed feedback Bragg grating in the optical cavity.
39. What is the cause of noise in the optical fiber communication system?
There are noise caused by unqualified extinction ratio, noise caused by random changes in light intensity, noise caused by time jitter, point noise and thermal noise at the receiving end, fiber mode noise, noise caused by pulse broadening caused by dispersion, and mode distribution noise of LD , The noise generated by the frequency chirp of the semiconductor laser and the noise generated by the reflection.
40. In the construction of the transmission network, what kind of optical fiber is mainly used? What are its main features?
There are three main types, namely G.652 conventional single-mode fiber, G.653 dispersion-shifted single-mode fiber and G.655 non-zero dispersion-shifted fiber.
G.652 single-mode fiber has relatively large dispersion in the C-band 1530-1565nm and L-band 1565-1625nm, generally 17-22psnm·km, and the system speed reaches 2.5Gbit/s or more, and dispersion compensation is required. At 10Gbit/s, the cost of dispersion compensation is very high. It is the most common optical fiber in the transmission network.
The dispersion of G.653 dispersion-shifted fiber in C-band and L-band is generally -1~3.5psnnm•km, and there is zero dispersion at 1550nm, and the system speed reaches 20gbit/s and 40Gbit/s respectively. It is single-wavelength ultra-long-distance transmission. The best fiber. But because DWDM has zero-dispersion characteristics, it will produce non-linear effects during expansion, leading to signal crosstalk and four-wave mixing FWM, so it is not suitable for DWDM.
G.655 non-zero dispersion-shifted fiber: G.655 non-zero dispersion-shifted fiber has a dispersion of 1-6 psnm·km in the C-band and 6-10 psnm·km in the L-band. The dispersion is very small, avoiding the zero dispersion zone. It can not only suppress FWM, but also can be used for DWDM expansion and high-speed systems. The effective area of the new G.655 fiber can be expanded to 1.5 times the effective area of the ordinary fiber, which can reduce the power density and nonlinear effects of the fiber.
41. What is fiber nonlinearity?
When the input optical power exceeds a certain value, the refractive index of the optical fiber will have a nonlinear relationship with the optical power, and Raman scattering and Brillouin scattering will occur, which will change the frequency of the incident light.
42. What effect does fiber nonlinearity have on transmission?
Non-linear effects will cause some additional losses and interference, which will degrade system performance. The WDM system has high optical power and long transmission distance along the optical fiber, resulting in nonlinear distortion. There are two types of nonlinear distortion: stimulated scattering and nonlinear refraction. Stimulated scattering includes Raman scattering and Brillouin scattering. These two kinds of scattering reduce the energy of incident light and cause loss. When the input power is very small, it can be ignored.
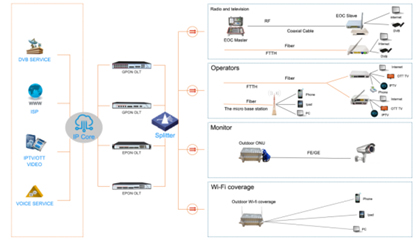
43. What is a passive optical network?
Passive Optical Network (PON) refers to the optical distribution network (ODN) between the OLT and the ONU without any active electronic equipment. It is a point-to-multipoint optical fiber transmission and access technology. The downlink adopts broadcast mode, and the uplink adopts time division multiple access mode, which can flexibly form tree, star, and bus topology structures. Only a simple optical splitter needs to be installed at the optical branch point, so it saves optical cable resources, Bandwidth resource sharing, saving machine room investment, fast network construction speed, low comprehensive network construction cost and other advantages. Passive optical networks include ATM-PON and Ethernet-PON.
Sopto produces and supplies various types of fiber optic cables, indoor and outdoor fiber optic cables, If you need fiber optic cables, or you have any questions about fiber optic cables, please feel free to contact us, [email protected] .
Related articles
1. System structure and topology of Passive Optical Network (PON)
2. What are PON system, OLT, ONU, ODN?
Tags : optical fiber,fiber optical cable,fiber cable,fiber
— END —